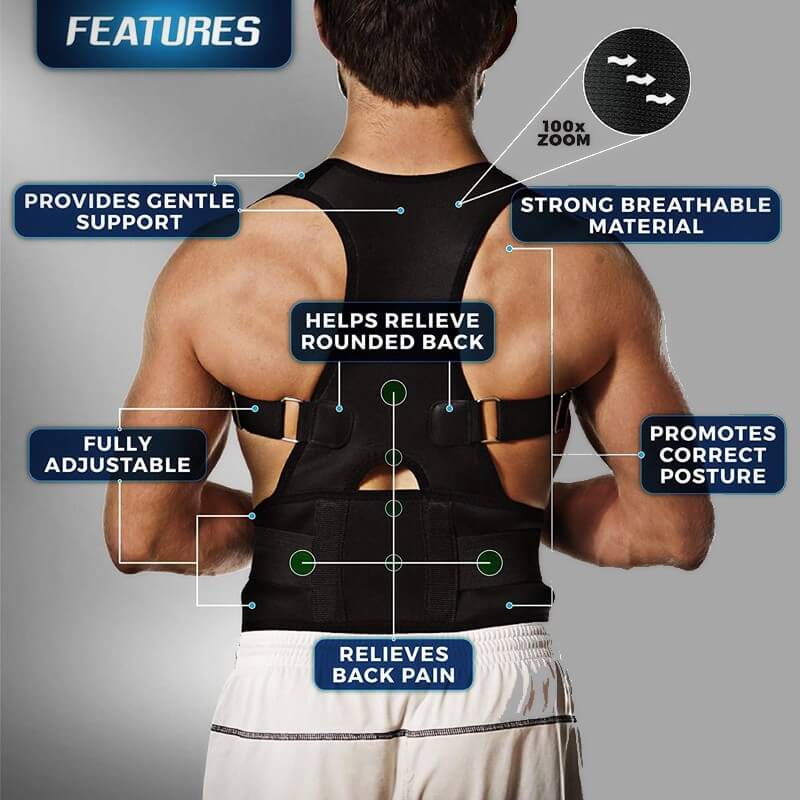
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare but serious medical condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves at the base of the spinal cord, known as the cauda equina, becomes compressed. This syndrome requires immediate medical attention to prevent long-term damage, including paralysis or loss of bladder and bowel control. Here’s everything you need to know about CES, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.

What is Cauda Equina Syndrome?
The cauda equina (Latin for "horse’s tail") is a collection of nerves located at the lower end of the spinal cord. These nerves control motor and sensory functions in the lower body, including the legs, bladder, and bowels. In cauda equina syndrome, compression of these nerves disrupts their function, leading to severe and potentially irreversible complications.
Common Causes of Cauda Equina Syndrome
- Herniated Discs:
- A ruptured or bulging disc in the lower spine is the most common cause of CES.
- Spinal Stenosis:
- Narrowing of the spinal canal can compress the cauda equina.
- Trauma:
- Injuries such as fractures or dislocations in the lower spine can lead to nerve compression.
- Tumors:
- Growths in the spine or spinal canal can press on the nerves.
- Infections or Inflammation:
- Conditions like spinal abscesses or meningitis may result in CES.
- Post-Surgical Complications:
- Rarely, complications from spinal surgery can lead to nerve compression.
- Other Conditions:
- Conditions like ankylosing spondylitis or a blood clot in the spinal canal.

Symptoms of Cauda Equina Syndrome
CES symptoms can develop suddenly or gradually. Early recognition is crucial. Common symptoms include:
- Severe Lower Back Pain:
- Often accompanied by pain radiating down one or both legs (sciatica).
- Saddle Anesthesia:
- Numbness or tingling in the areas that would touch a saddle, including the buttocks, inner thighs, and perineum.
- Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction:
- Difficulty urinating, loss of bladder or bowel control, or retention.
- Leg Weakness:
- Weakness in the legs, which may progress to paralysis.
- Sexual Dysfunction:
- Reduced sensation or function in the genital area.

Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis of CES is critical to prevent permanent nerve damage. Healthcare providers typically use:
- Physical Examination: Evaluating reflexes, muscle strength, and areas of numbness.
- Imaging Tests:
- MRI is the most common diagnostic tool to identify nerve compression.
- CT scans or X-rays may also be used in some cases.
Treatment Options for Cauda Equina Syndrome
Emergency Surgery:
- Decompression Surgery:
- Immediate surgical intervention is often required to relieve pressure on the cauda equina nerves. The sooner surgery is performed, the better the chances of recovery.
Post-Surgical Care:
- Physical Therapy:
- It helps regain strength and mobility in the lower body.
- Medications:
- Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antibiotics if an infection is present.
- Bladder and Bowel Management:
- Catheters or other aids may be necessary during recovery.
Long-Term Management:
- Some patients may experience residual symptoms despite successful treatment. Ongoing rehabilitation and assistive devices can help improve quality of life.
Preventing Cauda Equina Syndrome
While CES is not always preventable, you can reduce your risk by:
- Addressing Spinal Health Early:
- Seek prompt treatment for herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Practicing Safe Lifting Techniques:
- Avoid unnecessary strain on your lower back.
- Regular Exercise:
- Strengthen core and back muscles to support spinal health.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
- Reduces stress on the spine.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency. Seek immediate care if you experience:
- Sudden loss of bladder or bowel control
- Severe lower back pain with numbness in the saddle area
- Progressive weakness in your legs or difficulty walking
Final Thoughts
Cauda equina syndrome is a rare but serious condition that requires immediate intervention to prevent permanent damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to ensuring the best possible outcome. You can protect your spinal health and overall well-being by understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical care.
Your spine plays a vital role in your mobility and nerve function. Prioritize its care to maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.